Singleton - Creational Design Pattern
Like, every other post, lets start with our 3 prime questions. What, Why and How?
What is Singleton Design Pattern:
It is one of the creational design pattern.
Why it is used?
It is used to serve a purpose of avoiding a class creating multiple objects. It can only be used when a class should have a single instance available to all clients. If object creation frequency is high, Creating multiple objects sometimes proves costly. Singleton class is used for logging, database connection, driver objects, caching and thread pool.
How to use it?
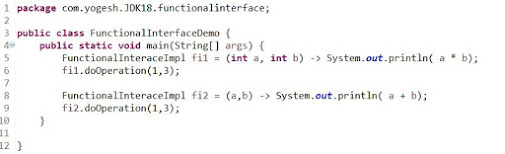
Please refer to the below screenshot on how we can implement singleton class
1. We need to create a Class which will work as singleton. In my case, the class name is SingletonClass.java
I'll explain you line by line to get a better understanding of implementation.
LINE NO 5: we have created a singletonClass object as private and static.
- private because we don't want anyone to access it from outside.
- static because we want to access it as a class level. If it is not declared as static then to access it, we may need to create an object of class. This explanation is partly dependent on LINE NO 12.
LINE NO 7: We have created constructor as private because we don't want anyone to create an object of this class from outside.(as we are creating this class based on a singleton principle)
LINE NO 12: As object can not be created from outside the class, hence while accessing it from outside
we have created a method getSingletonClassAPI as static. This method will give us an object of class singleton. This static method is justification of LINE NO 5, why we created the variable as static too.
Working:
- If the received argument of Class reference(i.e., SingletonClassObj) is not null, it will treat it as the object of class is already created and we don't need to create a new instance. Hence, it will return the same instance.
- On other hand, argument of class reference is null, then it will check if the object of the class i.e(singletonClass) is not null. If it is not null, then it will return the class object.
- If the Object of the class is also null then it will create a new instance of the class and return the same.
This way we can implement an singleton class
Below is the snapshot of the class which calls the API to create a singletonClass object.
As you can see, It print the same reference that means the same instance is always return.